Membrane Potential Is Best Described as
B The membrane keeps out Na and allows K and Cl- to pass more freely. C The membrane has a sodium-potassium pump that removes potassium from inside the cell and replaces it with sodium.

Membrane Potential Foundations Of Neuroscience
In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs.

. In biological membranes ionic pumps and channels originate ionic currents that separate the electric charges generating voltage gradients through the membrane Stein and Lieb 1986. The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential. Membrane potential also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell.
Neurons and muscle cells are excitable such that these cell types. The standard is to compare the inside of the cell relative to the outside so the membrane potential is a value representing the charge on the intracellular side of the membrane based on the outside being zero relatively speaking. 24 The equilibrium potential describes the membrane potential where what two forces are balanced.
Membrane potential is described as the charge difference between ions in and outside of the membrane producing the electrochemical gradie. Apart from the latter two which occur in excitable cells membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response. Key facts about the membrane potential.
In Figure 51Athe potassium concentration is greatinsidea nervefiber membrane but very low outside the membrane. A membrane potential is best describe O A chemical potential gradient of a neutral solute across a membrane An electrochemical potential gradient of an ion across a membrane A charge. Difference between intra- and extracellular ion concentration Na-K pump Permeability of the cell membrane for ions.
An action potential AP is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. If X fires 10 times and Y fires 10 times. Basic Physics of Membrane Potentials.
A density and magnetic B electrical and permeability C temperature and density D chemical and electrical E chemical and temperature Answer. That is there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges to move from the internal to exterior cellular environments and vice versa as long as there is no acquisition of kinetic energy or the. The cell membrane could best be described as a.
These movements result in different electrostatic charges across the cell membrane. This potential known as the cell membrane potential or simple membrane potential is found in most nerve cells and ranges between sixty and seventy-five millivolts mV. The resting membrane potential of a nerve cell is -70 mV which indicates that the intracellular region of the nerve cell has a negatively charged environment in comparison to the extracellular environment.
Sieve that lets fluids passively flow back and forth between the interior and exterior of the cell. Difference between the electric potential of the cellular membrane matrices when the cell isnt excited. A postsynaptic neuron has an RMP of -70mV and a typical threshold of -55mV.
The exact value measured for the resting membrane potential varies between cells but -70 mV is most commonly used as this value. Question 13 2 pts Resting membrane potential is best described as Separation of oppositely charged lons across a call membrane Voltage measured in resting cells that ranges from 50 to 30 m Separation of proteins across a cell membrane Voltage that results from difono negatively charged ions D Question 14 2 pts Chemical gradient across a cell. Membrane potential of a neuron when it is not transmitting any signal with respect to its immediate surrounding is called resting potential.
When X and Y are stimulated simultaneously the postsynaptic neuron depolarizes by 1 mV. A The cell membrane is semipermeable so it keeps in large negatively charged protein molecules. Let us assume that the membrane in this instance is permeable to the.
It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. Membrane potential unequal distribution if charges is at a resting excitable cell determined by the distribution of substances inside and outside of a neuron K diffusion is the most important. The membrane potential voltage is conventionally defined as Vϕinϕout where ϕin and ϕout are the potentials inside and outside the cell respectively.
The resting membrane potential is the result of the movement of several different ion species through various ion channels and transporters uniporters cotransporters and pumps in the plasma membrane. The resting membrane potential is changed to an action potential at 30 mV charge on it. Membrane Potentials Caused by Diffusion Diffusion Potential Caused by an Ion Concentration Difference on the Two Sides of the Membrane.
The minus sign depicts that the inner area is negative. Skin that provides a barrier between the interior and exterior of the cell. The membrane potential is a distribution of charge across the cell membrane measured in millivolts mV.
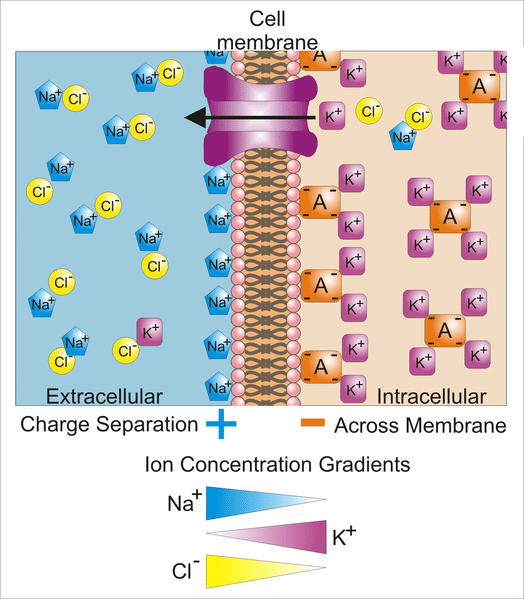
It has three presynaptic inputs-from neurons X Y and Z. The resting membrane potential ΔΨ of Xenopus. Charge separation across the membrane.
Or thousandths of a volt. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology 2010. With the ions distributed across the membrane at these concentrations the difference in charge is measured at -70 mV the value described as the resting membrane potential.
We learned that the movement of an ion across the membrane that is not balanced by the movement of a counter ion leads to charge separation across the membrane and that this charge separation forms the basis for the establishment of a potential difference across the plasma membrane ie membrane potential V m. Factors that determine it. D The summed charges of the unequally distributed ions.
Transmembrane potential Ψ is a physical property given by the differences in electric potential between two sites separated by a membrane. Generally the value of resting potential is -70mV. View the full answer.
The Romanians work was not as well-publicized. Stimulation of neuron X causes the postsynaptic neuron to depolarize by 05 mV. No one believed the Romanians had seen what they described.
Observation of the electrical potential difference across the cell membrane is described as a new method for monitoring apoptosis of a single cell. Thus option a is the right answer.

Chapter 7 Medical Education Physiology Membrane

Membrane Potential Foundations Of Neuroscience
Action Potential The Resting Membrane Potential Generation Of Action Potentials Teachmephysiology
No comments for "Membrane Potential Is Best Described as"
Post a Comment